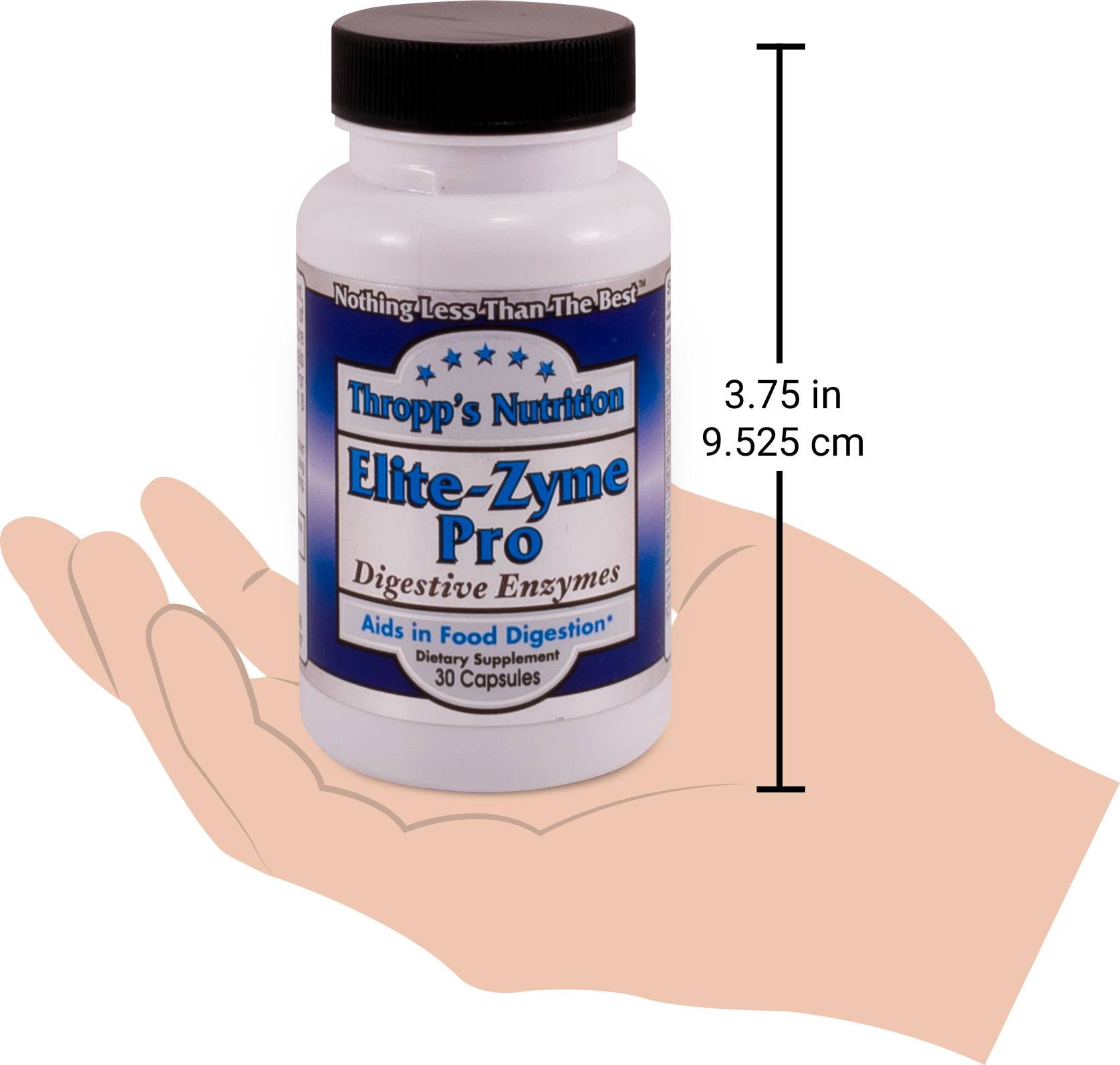
Elite-Zyme Pro
$79.00 – $780.00Price range: $79.00 through $780.00
TO ORDER PLEASE CALL 1-800-490-9067
Product Features
- Vegan Enzymes
- Gluten Free
- Vegetarian Capsules
- GMO Free
- No Fillers
- Made in the USA
- Natural Plant-Derived Enzymes
- Description
- What are Enzymes
- How to Take Digestive Enzymes and Ingredients
- How We Choose Which Ingredients to Use in Our Digestive Enzymes
- Why Digestive Enzymes are Important to You
- A Few Key Functions of Digestive Enzymes
- How to Find a High-Quality Digestive Enzyme
- Digestive Enzyme Comparison
- How to Compare Different Companies Digestive Enzymes
- The Differences Between the Elite-Zyme Ultra and Elite-Zyme Pro
Sound Familiar?
- Meal Fatigue
- Heartburn
- Constipation
- Bloating
- Lactose Intolerance
- Acid Reflux
- Irritable Bowel
- Food Sensitivities
- Crohn’s Disease
- Acid Blocking Drugs
- Diverticulitis D’s
- Food Allergies
- Weight Gain
- Diarrhea
- Gastritis
- GERD
You Aren’t What You Eat- You Are What You Can Absorb and Enjoy!
Remember when you could eat anything anytime you wanted?
Don’t Worry, You’re Not Alone. Many people of all ages experience digestive discomfort. Don’t miss out on enjoying a tasty meal with family and friends again. You don’t have to start a meal worried that you’re going to pay the price for eating it after you get done. Luckily, there’s plenty you can do to improve and boost your overall digestive health the natural way.
We want you to have healthy dietary habits such as drinking enough water, eating plenty of fiber, fruits and vegetables and so on. Yet even with the healthiest dietary habits some people need a little extra help. It takes a healthy digestive system to properly digest and absorb your food no matter how fresh and healthy the food is.
What are Enzymes
Where There Is Life – There Are Enzymes
You are alive because enzymes make it possible. Enzymes are the foundation of energy and the life force in all living things. Without enzymes, seeds would not sprout, fruit would not ripen, leaves would not change color, and you would not exist. Enzymes are responsible for building, detoxifying, and healing your body. They are the force that allows your body to digest and absorb food. Enzymes also regulate tens of thousands of other biochemical functions that take place every day in your body. These functions include breathing, growing, smelling, tasting, stimulating nerves, defending your body against disease, regulating hormones, and building organs, glands, and tissues. Even your thinking involves enzymes.
What are Enzymes
Enzymes are composed of long chains of amino acids held together by peptide bonds. Amino acids are derived from protein and serve as carriers for vital enzyme activity factors. Coenzymes, which come from essential vitamins and minerals, are needed for enzymes to function effectively. Vitamins are usually a structural component of enzymes. Enzymes are activated by trace mineral content. The activation produces electrical charges so that attractions and repulsions of charged particles occur within the enzymes.
Cooking Food Kills All Enzymes
 The most serious threat to the body’s supply of natural enzymes is the habit of eating cooked and processed foods. Cooking or processing food over 118 degrees totally destroys the enzymes in the food. You will not find enzymes in foods that are in a box, bottle, or can. Cooking also contributes to nutrient loss. Pasteurization, sterilization, radiation, freezing, and microwaving either render food enzymes inactive or alter their structure.
The most serious threat to the body’s supply of natural enzymes is the habit of eating cooked and processed foods. Cooking or processing food over 118 degrees totally destroys the enzymes in the food. You will not find enzymes in foods that are in a box, bottle, or can. Cooking also contributes to nutrient loss. Pasteurization, sterilization, radiation, freezing, and microwaving either render food enzymes inactive or alter their structure.
Early Signs of Enzyme Deficiency
Early signs of enzyme deficiency are digestive complaints such as heartburn, gas, bloating and belching. Other symptoms may include headaches, stomach aches, diarrhea, constipation, chronic fatigue, yeast infections, and nutritional deficiencies. Because these symptoms are so prevalent, many people consider them to be normal. However, they are an indication that the body cannot process the food eaten. Digestive problems concern the stomach, intestines, colon, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder.
Death Begins in the Colon
 Enzymes and fiber are essential for proper digestion and elimination. Sadly, the typical American diet is generally significantly lacking in these requirements. Fiber acts as a bulking agent and speeds transit time of food in the digestive tract. These actions prevent metabolic waste from creating toxic by-products. A major benefit of fiber is that it binds acids to bile and carries the bile along with excess fats out of the body. Fiber helps to lower cholesterol, reduce the risk of heart disease, lower blood pressure, improve blood sugar, and promote the growth of friendly intestinal flora. It also promotes bowel regularity, aids digestion, and helps to keep the bowel clean.
Enzymes and fiber are essential for proper digestion and elimination. Sadly, the typical American diet is generally significantly lacking in these requirements. Fiber acts as a bulking agent and speeds transit time of food in the digestive tract. These actions prevent metabolic waste from creating toxic by-products. A major benefit of fiber is that it binds acids to bile and carries the bile along with excess fats out of the body. Fiber helps to lower cholesterol, reduce the risk of heart disease, lower blood pressure, improve blood sugar, and promote the growth of friendly intestinal flora. It also promotes bowel regularity, aids digestion, and helps to keep the bowel clean.
Fiber cannot do its job effectively unless enzymes do theirs. Over time, hard-to-digested high-protein foods (such as cooked meat and other enzyme-deficient foods) exhaust the digestive organs until they can no longer function efficiently. This results in the accumulation of partially digested food in the bowel. By middle age many people have as much as 20 pounds of undigested, putrefactive food in their colon. Toxins produced from this putrefactive buildup are reabsorbed into the bloodstream, creating autointoxication, or self -poisoning. This results in a dramatically weakened immune system and can lead to serious debilitating health problems including colon cancer. Supplemental food enzymes taken with meals and between meals can work to help eliminate the accumulation of toxic wastes in the stomach and colon.
Blood Under the Microscope
 Enzymes act as scavengers of foreign substances throughout the body preventing joints from gumming up and arteries from clogging. Enzymes in the body’s white blood cells are responsible for destroying foreign, disease-producing substances in the blood and lymph. During illness and infection, white blood cells increase to fight off pathogens. When cooked foods are eaten, the body reacts just as though we had an acute illness. Within 30 minutes of eating cooked foods, our white-blood-cell count increases dramatically. This means that the immune system is being unnecessarily called into action virtually every time we eat.
Enzymes act as scavengers of foreign substances throughout the body preventing joints from gumming up and arteries from clogging. Enzymes in the body’s white blood cells are responsible for destroying foreign, disease-producing substances in the blood and lymph. During illness and infection, white blood cells increase to fight off pathogens. When cooked foods are eaten, the body reacts just as though we had an acute illness. Within 30 minutes of eating cooked foods, our white-blood-cell count increases dramatically. This means that the immune system is being unnecessarily called into action virtually every time we eat.
Studies show that mobilization and increase of white blood cells do not happen when raw food is consumed. Molecules from improperly digested proteins and fats that are small enough to get into the blood, but too large to get into the cells, are called floating immune complexes. They are now considered toxic invaders in the body instead of nutrients.
The dark field microscope is a viable technology used for live blood analysis. This microscope can magnify a tiny drop of blood 15,000 times and can give an accurate picture of floating immune complexes. Let’s take a look at some of the unhealthy conditions we can see under this microscope. We see red blood cells sticking together, which results in a lack of surface area and creates low oxygen content. This can lead to chronic fatigue, migraine headaches, and poor circulation. We see cholesterol and uric acid crystals, which could eventually lead to arthritis or gout. We see plaque due to undigested fats, which can lead to arteriosclerosis. We see free radical damage, which can have devastating consequences. It takes a concentrated effort from white blood cells to digest floating immune complexes and protect our body from other toxic invaders. Meanwhile the organs, tissues, and glands are robbed of their rightful share of needed enzymes.
Enzymes and Weight Loss
 One of the primary keys to weight loss may simply be the action of enzymes. Dr. David Galton at Tufts University School of Medicine tested people weighing 230-240 pounds. He found that virtually all of them were lacking lipase enzymes in their fatty tissues. Lipase, found abundantly in raw foods, is a fat-splitting enzyme that aids the body in digestion, the storage and distribution of fat, and the burning of fat for energy. Lipase activity breaks down and dissolves fat throughout the body. Without lipase, fat stagnates and accumulates in the organs, arteries, and capillaries. You will see it on hips, thighs, buttocks and stomach, etc.
One of the primary keys to weight loss may simply be the action of enzymes. Dr. David Galton at Tufts University School of Medicine tested people weighing 230-240 pounds. He found that virtually all of them were lacking lipase enzymes in their fatty tissues. Lipase, found abundantly in raw foods, is a fat-splitting enzyme that aids the body in digestion, the storage and distribution of fat, and the burning of fat for energy. Lipase activity breaks down and dissolves fat throughout the body. Without lipase, fat stagnates and accumulates in the organs, arteries, and capillaries. You will see it on hips, thighs, buttocks and stomach, etc.
A good example of the importance of lipase activity lies in an interesting experiment with pigs. Veterinarians fed one group of pigs only enzyme-rich raw potatoes and another group enzyme deficient cooked potatoes. The pigs eating the raw potatoes did not get fat. However, the pigs eating cooked potatoes gained weight rapidly. The regular use of digestive food enzymes that include lipase with meals often results in shedding excess pounds.
Sugar
 What about sugar? Unprocessed raw sugar contains enzymes, chromium, and B vitamins and is easily digested and assimilated. White processed sugar contains no enzymes, no B vitamins, and no chromium. In order for the body to metabolize processed sugar, the missing vitamins and chromium must be stolen from the body’s own tissue stores. If large quantities of white sugar are eaten, then not only are the body’s enzymes depleted, but we suffer B vitamin and chromium deficiencies. Chromium is an essential mineral needed by the body to support efficient insulin function. Insulin regulates the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. Studies show a relationship between obesity and chromium deficiencies. B vitamins are considered coenzymes essential to the metabolism of all cells.
What about sugar? Unprocessed raw sugar contains enzymes, chromium, and B vitamins and is easily digested and assimilated. White processed sugar contains no enzymes, no B vitamins, and no chromium. In order for the body to metabolize processed sugar, the missing vitamins and chromium must be stolen from the body’s own tissue stores. If large quantities of white sugar are eaten, then not only are the body’s enzymes depleted, but we suffer B vitamin and chromium deficiencies. Chromium is an essential mineral needed by the body to support efficient insulin function. Insulin regulates the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. Studies show a relationship between obesity and chromium deficiencies. B vitamins are considered coenzymes essential to the metabolism of all cells.
Candidiasis and Allergy Relief
 Candidiasis adversely affects the endocrine system and nervous system and has a devastating effect on the immune system. Candidiasis is an overgrowth of common yeast that lives in the intestinal track. Yeast overgrowth is triggered by the killing off of friendly bacteria in the intestinal tract, which generally keeps it under control. It is estimated that at least 50% of the population may be affected by this condition.
Candidiasis adversely affects the endocrine system and nervous system and has a devastating effect on the immune system. Candidiasis is an overgrowth of common yeast that lives in the intestinal track. Yeast overgrowth is triggered by the killing off of friendly bacteria in the intestinal tract, which generally keeps it under control. It is estimated that at least 50% of the population may be affected by this condition.
Candidiasis and allergies affect millions of people. Cause and prevention of both conditions are similar. Allergens and antigens such as viruses, bacteria, fungi, and yeast are most often proteins. They enter the body via the digestive tract. Allergens may also be breathed into the body via the lungs. Protease is a digestive enzyme needed in tremendous quantities to digest and eliminate these toxic invaders, not only in the digestive tract but in the bloodstream as well. Most antigens, including yeast, can be eliminated by taking supplemental enzymes with meals and between meals. It is also advisable to take supplements that will help to reestablish friendly intestinal flora.
How to Take Digestive Enzymes and Ingredients
Suggested use: Take 1 capsule with each meal.
 The best time to take digestive enzymes is first thing when you sit down to eat. Digestive enzymes can be taken during the meal, but it is best if they take them before. If you forget to take them before or during the meal you can still take them after the meal, they will not go to waste.
The best time to take digestive enzymes is first thing when you sit down to eat. Digestive enzymes can be taken during the meal, but it is best if they take them before. If you forget to take them before or during the meal you can still take them after the meal, they will not go to waste.
Digestive Enzymes can also be taken on an empty stomach. The reason for doing this is to help eliminate undigested food throughout the digestive system. Undigested food begins to rot and ferment which can start polluting the bloodstream with harmful toxins. Not only do many people feel better and have more energy, they lose weight.
The difference between our Elite-Zyme Ultra and our Elite-Zyme Pro. Both digestive formulas are capable of digesting proteins, carbs, fibers, sugars, dairy, and fats. The difference between our two enzyme formulas is that the Elite-Zyme Ultra is designed more for someone who has problems digesting dairy products.
The strength of an enzyme ingredient is determined by its units of activity, not milligrams. Units of activity express the ingredients strength. Milligrams only express the amount of an ingredient.
For example, an enzyme product could contain 250mg of protease enzyme with a strength of only 30,000 FCC/HUT OR the same 250mg of protease enzyme could have the strength of 150,000 FCC/HUT. In this example, there is a 5-time difference in the amount of enzyme strength. Another way to say this is that the more units of activity in a formulation, the more food it is capable of digesting, regardless of the number of milligrams of an ingredient.
Units of activity are based on the Food Chemical Codex (FCC), Academy of Sciences and accepted by the American Food Industry.
How We Choose Which Ingredients to Use in Our Digestive Enzymes
 When most companies formulate a digestive enzyme product, they’ll buy all of the ingredients from ONE ingredient supplier. (There are many ingredient suppliers.) Then the ingredients are sent to the manufacturer to be encapsulated and bottled before being shipped to the retail or wholesale company. The problem with this is that all of the enzymes such as protease, amylase, lipase, etc come from ONE supplier. This supplier may sell for example, the best protease or amylase on the market but not the highest quality lipase or lactase. Therefore, their product may contain a few high quality ingredients but also contain some lower quality ingredients.
When most companies formulate a digestive enzyme product, they’ll buy all of the ingredients from ONE ingredient supplier. (There are many ingredient suppliers.) Then the ingredients are sent to the manufacturer to be encapsulated and bottled before being shipped to the retail or wholesale company. The problem with this is that all of the enzymes such as protease, amylase, lipase, etc come from ONE supplier. This supplier may sell for example, the best protease or amylase on the market but not the highest quality lipase or lactase. Therefore, their product may contain a few high quality ingredients but also contain some lower quality ingredients.
All of us come across this in our lives on a daily basis. For example, a vehicle manufacturer may produce the best pick-up trucks, but a different vehicle manufacturer may produce the best cars. We recognize this and when formulating our digestive enzymes we search around for the highest quality ingredients. We purchase the best ingredients from SEVERAL different ingredient suppliers and send them to our manufacturer for encapsulation and bottling. This ensures that every ingredient in our product is of the highest quality.
When choosing which ingredient suppliers to use, we have SEVERAL of them send us samples of the highest quality enzymes they sell. Such as protease, amylase, lipase, etc. After determining which enzymes are the highest quality, we formulate our enzyme products. This process leads us to using several different ingredient suppliers instead of only one like most companies. This is how we formulate higher quality digestive enzyme products.
Why Digestive Enzymes are Important to You
Enzymes are what your body naturally uses to digest the food you eat. There are TWO ways your digestive system receives the enzymes you need. The first way is that the enzymes are naturally in the foods you eat or secondly, they are produced by your digestive organs. Chances are you may need a little help in getting the enzymes your body needs.
Why? – Two Main Reasons
First, researchers have discovered that cooking or processing food over 118 degrees Fahrenheit, kills virtually all digestive enzymes that were naturally in it. Second, as we age our bodies ability to produce enzymes slowly diminishes. These two factors can put you at risk for a variety of health imbalances.
To compensate for these two factors your body must work overtime to produce enzymes. If you’ve ever felt sluggish after a meal, it’s possibly because your body is working overtime to digest the food that you have just consumed.

When your body works overtime to properly digest your food, it doesn’t have as much energy to devote to other functions, such as immune defense and degenerative disease defense. Don’t let your health suffer because your body is compensating for enzyme deficient food. Simply replace some of the enzymes by taking an enzyme supplement with your meal. When food is properly digested, fewer digestive imbalances occur.
Enzymes are the natural workforce of the body and your digestive system is at the root of your overall health. Supplementing with enzymes helps compensate for enzyme deficient foods. By properly digesting your food you’ll get more nutrition out of your food, and allow your digestive organs to spend more time on keeping your body healthy and less time on digestion. Digestive enzymes are crucial for both healthy and unhealthy diets.
Many medications merely mask digestive symptoms without addressing any possible underlying issues. Consider digestive enzyme supplements – the natural solution for digestive health.
Can you relate to any of the following:
- Avoid certain foods?
- Feel tired after a meal?
- Feel bloated after a meal?
- Avoid certain restaurants?
- Experience digestive discomfort?
- Have irregular bowel movements?
- Have a mental list of foods you can’t eat?
A Few Key Functions of Digestive Enzymes
 Undigested food begins to ferment and rot in the intestines and colon, this decaying process leads to the buildup of harmful toxins which enter the rest of our body. These toxins can cause fatigue, pre-mature aging, and numerous degenerative diseases. Most of us have experienced this fatigue after a large meal. Nutrient absorption is hindered by undigested food that has stuck to our intestinal walls.Digestive enzymes help break down this undigested food.
Undigested food begins to ferment and rot in the intestines and colon, this decaying process leads to the buildup of harmful toxins which enter the rest of our body. These toxins can cause fatigue, pre-mature aging, and numerous degenerative diseases. Most of us have experienced this fatigue after a large meal. Nutrient absorption is hindered by undigested food that has stuck to our intestinal walls.Digestive enzymes help break down this undigested food.
Digestive enzymes may also help with obesity. Many health professionals believe that a low level of lipase in fatty tissue may contribute to obesity. If the lipase in the digestive enzyme supplement is not used up in the role of digestion during the meal it may be stored in the liver for future use such as digesting stored fat. This is crucial because of the correlation between obesity and Type II diabetes, hypertension, breast cancer and other prevalent American diseases. Digestive enzymes can play a vital role in improving the immune system by reducing metabolic stress on the digestive system. They may also help break down fatty deposits that build up around the inside of blood vessels, which restrict blood flow. When food is not completely broken down the undigested proteins, fats, and minerals can form uric acid crystals that may lead to kidney stones and joint pain.
Why We Need Digestive Enzymes
 1. The body produces two types of enzymes, metabolic and digestive. When you eat cooked or processed foods, nearly all food enzymes are destroyed which forces the body to supply all of the needed digestive enzymes, which can overstress the pancreas and its ability to also produce metabolic enzymes (enzymes needed for all bodily functions). Food that is cooked over 118 degrees contains almost no functioning digestive enzymes.
1. The body produces two types of enzymes, metabolic and digestive. When you eat cooked or processed foods, nearly all food enzymes are destroyed which forces the body to supply all of the needed digestive enzymes, which can overstress the pancreas and its ability to also produce metabolic enzymes (enzymes needed for all bodily functions). Food that is cooked over 118 degrees contains almost no functioning digestive enzymes.
2. Approximately one-third of the body’s energy is spent digesting food. People with poor digestion can expend even more energy trying to digest food properly. The less energy the body spends on digesting food the less hungry you will feel, and the more energy you will have.
How to Find a High-Quality Digestive Enzyme

Once you know why digestive enzymes are important, it’s equally important to know how to find a high-quality product. Thropp’s Nutrition utilizes only natural plant-derived enzymes which enables the enzymes to work in a wider pH range than other forms of digestive enzymes such as animal derived.
A product that can function in a wide pH range is important because the pH in the lower stomach can reach as low as1.5 and the pH in the small intestine can reach as high as 8. It is also important that a digestive enzyme supplement contains Ionic Trace Minerals. Why? Because ionic trace minerals act as cofactors to increase the utilization of digestive enzymes.
Our enzymes are designed to improve digestion of foods whether cooked, processed or natural. The Elite-Zyme Ultra digestive enzyme is a full spectrum high potency formulation capable of aiding in the digestion of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, sugars, fibers, and dairy products. Our enzymes are produced in an Organically Certified facility that is FDA inspected and contains no fillers, yeast, dairy, wheat, soy, or corn and is free of artificial colors, flavors, and preservatives. We use the highest quality ingredients to produce superior results the natural way.
Here are a few common reasons that can diminish your enzyme reservoir:
- The aging process – as we age our enzyme producing capabilities may not be as robust as they once were.
- Food additives and preservatives.
- Years of eating cooked and processed food that is enzyme deficient.
- Incorrect proportions of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
- Inadequate vitamin and mineral intake.
- Poor eating habits such as eating when stressed, not thoroughly chewing food, eating too quickly.
- You didn’t get this way overnight. It’s gonna take commitment to get better.
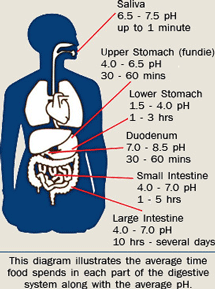
The diagram illustrates the average time food spends in each part of the digestive system along with the average pH
 The pH is a way of measuring how acidic or alkaline the body is. The pH in the human digestive tract varies greatly. The pH of saliva is usually between 6.5 to 7.5. After we chew and swallow food it then enters the upper portion of the stomach which has a pH between 4.0 to 6.5. This is where “predigestion” occurs while the lower portion of the stomach is secreting hydrochloric acid (HCI) and pepsin until it reaches a pH between 1.5 to 4.0. After the food mixes with these juices it then enters the duodenum (small intestine) where the pH changes to 7.0 to 8.5. This is where 90% of the absorption of nutrients is taken in by the body while the waste products are passed out through the colon (pH 4.0 to 7.0).
The pH is a way of measuring how acidic or alkaline the body is. The pH in the human digestive tract varies greatly. The pH of saliva is usually between 6.5 to 7.5. After we chew and swallow food it then enters the upper portion of the stomach which has a pH between 4.0 to 6.5. This is where “predigestion” occurs while the lower portion of the stomach is secreting hydrochloric acid (HCI) and pepsin until it reaches a pH between 1.5 to 4.0. After the food mixes with these juices it then enters the duodenum (small intestine) where the pH changes to 7.0 to 8.5. This is where 90% of the absorption of nutrients is taken in by the body while the waste products are passed out through the colon (pH 4.0 to 7.0).
Our enzymes are designed to improve digestion of foods whether cooked, processed or natural. They also help eliminate toxins from the blood by breaking down undigested foods. Almost all of the food we eat (90% or higher) is composed of proteins, carbohydrates, or fats. Therefore a good quality digestive enzyme should contain a large amount of protease, amylase, lipase, and acid stable protease. These three ingredients should be the first three ingredients looked at when comparing digestive enzymes. The other enzymes in the formulation are important for the proper assimilation of less common but essential nutrients. This is a high activity formulation designed to be what we believe as the most potent and well rounded digestive enzyme on the market.
Digestive Enzyme Comparison
Compare for Yourself!
Listed below are the main and most important enzymes in each product we believe to be for breaking down Protein, Carbohydrates, Fats and Fiber. Below is what each company’s capsule contains for the enzymes that are listed on the chart, there are of course other enzymes in our product as well as the other company’s. There is just not enough room to list all of them.
Note: When measuring Lipase activity that each FIP unit is up to 5 to 10 times more potent than when measuring Lipase activity in LU. If you would like another product added send us an empty bottle and the Retail Cost and we will add it to this chart.
| Company Name Product Name | Protease (HUT) | Acid Stable Protease (SAPU) | Amylase (SKB/DU) | Lipase (FIP/LU) | Cellulase (CU) | Retail Cost | Cost per Capsule (ea.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thropp's Nutrition Elite-Zyme Pro | 150,000 | 250 | 20,000 | 5,000 FIP | 3,000 | $69.00 270 capsules | $0.26 |
| Garden of Life Q-Zyme Ultra | 80,000 | 15 | 25,000 | 5,000 FIP | 725 | $26.97 90 capsules | $0.30 |
| Enzymedica Digest Gold | 80,000 | n/a | 23,000 | 3,500 FIP | 3,000 | $99.98 240 capsules | $0.42 |
| Theramedix DGX 120 | 70,000 | n/a | 22,000 | 3,000 FIP | 600 | $64.99 120 capsules | $0.42 |
| Thropp's Nutrition Elite-Zyme Ultra | 75,000 | 175 | 12,000 | 2,000 FIP | 1,000 | $24.00 90 capsules | $0.27 |
| Swiss Labs Active Zyme | 33,250 | 0 | 6,000 | 400 LU | 660 | $49.97 60 capsules | $0.83 |
| Enzymedica Digest | 42,000 | n/a | 12,000 | 500 FIP | 200 | $57.98 240 capsules | $0.24 |
| Theramedix DGT 120 | 42,000 | n/a | 12,000 | 500 FIP | 200 | $26.99 90 capsules | $0.30 |
| Pure Prescription D-Enzymes | 450 | na | 1800 | 75 LU | 15 | $30.00 90 capsules | $0.33 |
| Nature Sunshine Proactazyne Plus | 11,000 | 8 | 2,100 | 12 FIP | 60 | $18.50 100 capsules | $0.19 |
| Nutraceutical Science Institute Digestive Enzymes | 82,000 | n/a | 8,000 | 90 FIP | 600 | $14.99 90 capsules | $0.17 |
| Baseline Nutritionals Digestive Enzymes | 40,000 | 1,500 | 16,000 | 1,400 FIP | 750 | $34.95 90 capsules | $0.39 |
| New Sun Master Zyme | 28,000 | n/a | 13,000 | 120 FIP | 400 | $25.80 100 capsules | $0.26 |
| Dr. Newtons Nu-Zymes | 6,000 | n/a | 2,500 | 50 LU | 50 | $44.95 90 capsules | $0.50 |
| Wellzymes Digestive Health | 25,000 | n/a | 10,000 | 200 LU | 450 | $16.99 60 capsules | $0.28 |
| Houston Enzymes | 45,000 | n/a | 6,000 | 100 | 0 | $45.50 180 capsules | $0.25 |
| HealthForce Nutritionals Digestive Enhancement Enzymes | 12,500 | 200 | 2,500 | 400 LU | 500 | $18.95 120 capsules | $0.15 |
| Rainbow Minerals ThetaZyme | 45,000 | 120 | 8,500 | 5,000 Lu | 360 | $29.95 120 capsules | $0.25 |
| Whole Earth Health Quadra-Zyme Plus | 45,000 | n/a | 9,000 | 1500 Lu | 1,000 | $34.00 180 capsules | $0.18 |
| Standard Process Multizyme | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | $36.67 150 capsules | $0.24 |
| Natural Brand Super Digestive Enzymes | 7,500 | 0 | 3,500 | 125 LU | 50 | $10.99 100 capsules | $0.11 |
| Shaklee EZ-Gest | 12,500 | 0 | 2,000 | 150 LU | 0 | $22.45 30 capsules | $0.75 |
| RGarden Int. Quadra-zyme Plus | 45,000 | n/a | 9,000 | 1,500 LU | 1,000 | $34.00 180 capsules | $0.19 |
| Brantley Active Enzymes Plus | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | $29.99 60 capsules | $0.50 |
| Global Health Treat Active Digestive Enzymes | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | $39.99 90 capsules | $0.44 |
| Bragg Superior Systemic Enzymes | n/a | n/a | n/a | 1,500 LU | n/a | $39.99 120 capsules | $0.33 |
| Source Naturals Essential Enzymes | In mg | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | $7.40 60 capsules | $0.12 |
| Prolipamy Super Digestive Care | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | $39.95 60 capsules | $0.67 |
| Enzymatic Therapy | 45,800 | n/a | 11,900 | 1,250 | 210 | $38.95 180 capsules | $0.22 |
| Natural Wellness Centers of America Ultra-Enzyme Support | 13,000 | 10 | 1500 | 20 LU | 87.5 | $30.99 200 capsules | $0.34 |
| Phyto-Opti-Zymes | 38,675 | 53 | 11,025 | 1,500 LU | 1,000 | $60.00 200 capsules | $0.30 |
| Twin Lab Super Enzyme Caps | Animal & Plant Enzymes | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | $17.69 200 capsules | $0.09 |
| Nature's Plus Ultra-Zyme | Animal Enzymes | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | $28.10 180 tablets | $0.11 |
| Nature Sunshine Food Enzymes | Animal & Plant Enzymes | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | $22.85 120 tablets | $0.13 |
| Nutri Health MetaboZyme Proprietary Blend | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | $39.95 90 capsules | $0.44 |
| Jigsaw Digestive Enzymes | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | $49.97 180 capsules | $0.27 |
| GNC Super Digestive Enzyme | 8,500 | 8 | 3,500 | 125 LU | 50 | $10.99 1000 capsules | $0.10 |
| Eniva Digest-EZ | 45,000 | 120 | n/a | n/a | n/a | $40.45 120 capsules | $0.33 |
How to Compare Different Companies Digestive Enzymes
 Our digestive enzyme formulations are listed in units of activity. The potency of a digestive enzyme product is determined by the units of activity. The units of activity express the strength of the enzymes in the formulation. Another way to say this is that the more units of activity in a formulation, the more food it is capable of digesting.
Our digestive enzyme formulations are listed in units of activity. The potency of a digestive enzyme product is determined by the units of activity. The units of activity express the strength of the enzymes in the formulation. Another way to say this is that the more units of activity in a formulation, the more food it is capable of digesting.
Units of activity are based on the Food Chemical Codex (FCC), Academy of Sciences and accepted by the American Food Industry. For example, the amount of Protease in the Elite-Zyme Pro is 150,000 HUT. This means that each capsule has 150,000 units of activity. Using these units of activity to compare different digestive enzymes is crucial. The units of activity in a product are what counts, not the number of milligrams or another measuring system. What’s important is the amount of food the product can digest. When comparing our product with others, and they don’t use the Food Chemical Codex (FCC), it’s almost impossible to compare the two products. So when using other products that don’t use the Food Chemical Codex, ask them what is the activity level equivalent to the Food Chemical Codex.
It is impossible to compare proprietary blend products to any other. A proprietary blend is a mixture of the ingredients stated in the blend. The only thing the proprietary blend product states is the total amount of blend. They don’t state the amount of each ingredient or its activity level. Therefore, you don’t know what the activity level of each enzyme is, and this is the only measurement that is used when the supplier sells to the manufacturer for encapsulating the enzyme. You wouldn’t buy a car if they wouldn’t tell you the size of the engine. For example, the ingredient supplier of the enzyme can sell 250mg that would equal 25,000 FCC/HUT of protease enzyme, or 250mg that would equal 150,000 FCC/HUT of protease enzyme. In this example there is a 6 time difference in the amount of enzyme strength.
This is how some nutritional companies might mislead their customers in order to increase their profit margin. They may use lower cost ingredients, and formulate a product with weaker/lower activity enzymes and label the product as a proprietary blend or list the ingredients individually in mg. So when considering to buy a product that states a proprietary blend or ingredients listed in mg, ask for a copy of the certificate of analysis that comes from the lab. Don’t let yourself be misled by a company using different terminology. Always know the quality/activity level of each ingredient in the product. Take a look for yourself and see how our product stands up next to others sold nationwide. We don’t mislead our customers.